Assume servers are compromised
MindooDB is designed so that storage and sync infrastructure can be untrusted. Clients encrypt before sync and prove authorship with signatures.
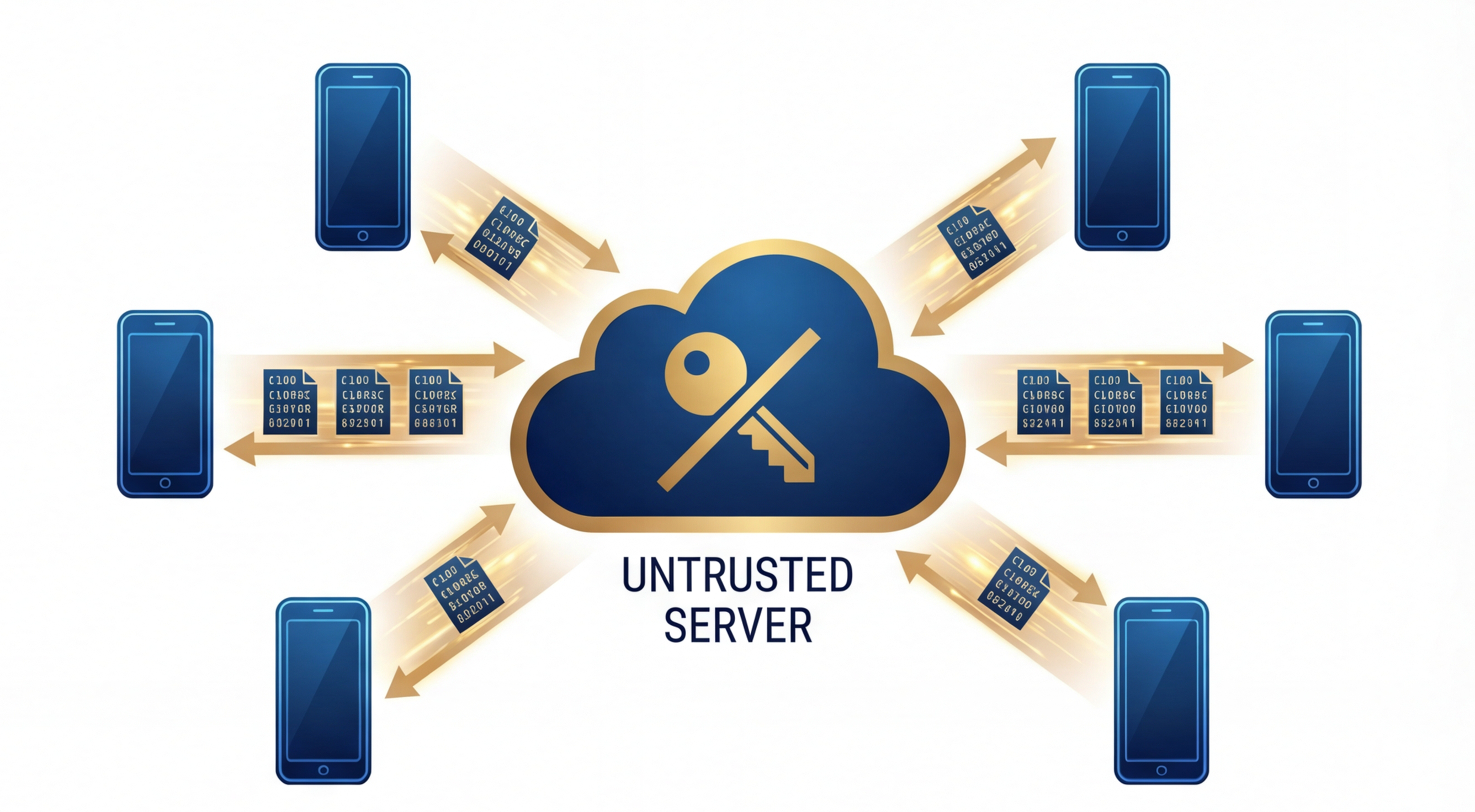
Changes and attachments are encrypted before leaving the device (AES-256-GCM).
Every change is signed (Ed25519) to prove authorship and prevent tampering.
Entries are append-only and chained, supporting audit trails and time travel.
Access control
Documents are encrypted with a default tenant key unless you choose a named key for fine-grained access. Named keys can be shared only with specific users.
Servers can validate which signing keys are trusted without decrypting business documents, using a minimal-access tier.
Regulatory compliance capabilities
MindooDB's append-only architecture, end-to-end encryption, and cryptographic integrity make it suitable for meeting regulatory compliance requirements across industries.
- End-to-end encryption ensures patient data is never visible to servers
- Complete audit trails document who accessed what and when
- Access controls with fine-grained permissions for different roles
- Data retention policies supported through archival strategies
- Immutable records through append-only architecture
- Cryptographic integrity proves records haven't been altered
- Complete transaction history for audit requirements
- Time travel to reconstruct any historical state
- Right to be forgotten via
purgeDocHistory()method - Data portability through export capabilities
- Access logging for complete audit trails
- Data protection by design through end-to-end encryption
- Payment card data protection through document-level encryption
- Access controls with named keys for restricted access
- Audit trails for all access and changes
- Encryption of sensitive payment data
- ✅ Complete change history (append-only)
- ✅ Cryptographic signatures (authorship proof)
- ✅ Tamperproof records (hash-chained)
- ✅ Time travel (reconstruct any state)
- ✅ End-to-end encryption (server can't decrypt)
- ✅ Fine-grained access control (named keys)
- ✅ Access logging (who accessed what)
- ✅ Data retention policies (archival support)
Security guarantees
- Signing: Ed25519 (elliptic curve, 128-bit security)
- Transport encryption: RSA-OAEP with SHA-256 (3072-bit keys)
- Payload encryption: AES-256-GCM (256-bit security)
- Token signing: HMAC-SHA256
- Authenticity: Ed25519 signatures prove authorship
- Integrity: Hash chaining prevents tampering
- Confidentiality: AES-256-GCM encryption protects content
- Non-repudiation: Cryptographic signatures are unforgeable
Read the detailed security audit documentation for comprehensive threat analysis and security considerations.
Read more: Revocation timestamp protection.